Register now and start:
- Accessing PAR Training
- Shopping PAR products & tools
- Using online assessments with PARiConnect
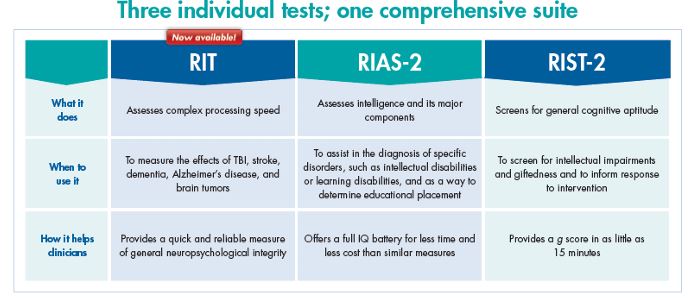
The RIT is a Stroop-style test of complex processing speed that measures general neuropsychological integrity. It adds a layer of cognitive processing tasks—inhibition and attention-shifting—to simple tasks, which makes them more complex and thus more indicative of cognitive flexibility and selective attention.
The RIT gives examiners full confidence in making accurate comparisons of performance using highly reliable scores derived from a common sample—it’s the best of all possible psychometric worlds.
—Cecil R. Reynolds, PhD, RIT coauthor
The mental effort required for the RIT allows clinicians to measure the effects of TBI, stroke, brain insult or injury, dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and brain tumors. Alternately, the RIT can be used as a measure of attention and complex processing speed deficits and as a rapid means of measuring recovery from concussion.
Features and benefits